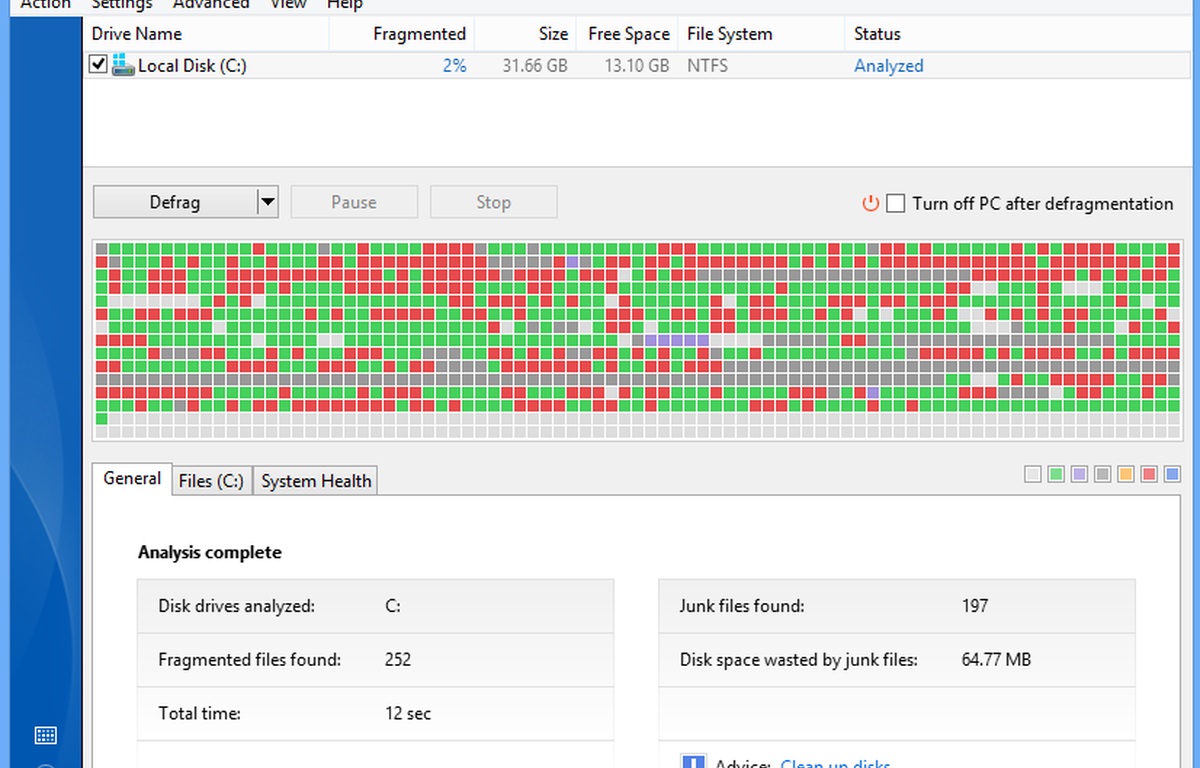
However, the same is not clear to many as to what disk defragmentation entails. All the info you get from Windows is that Disk Defragmentation and Drive Optimization will make your hard disk perform better. This begs the question, what is disk fragmentation and how does it happen? Read More: 10 quick ways to make your Windows PC run faster
Causes Of Disk Fragmentation
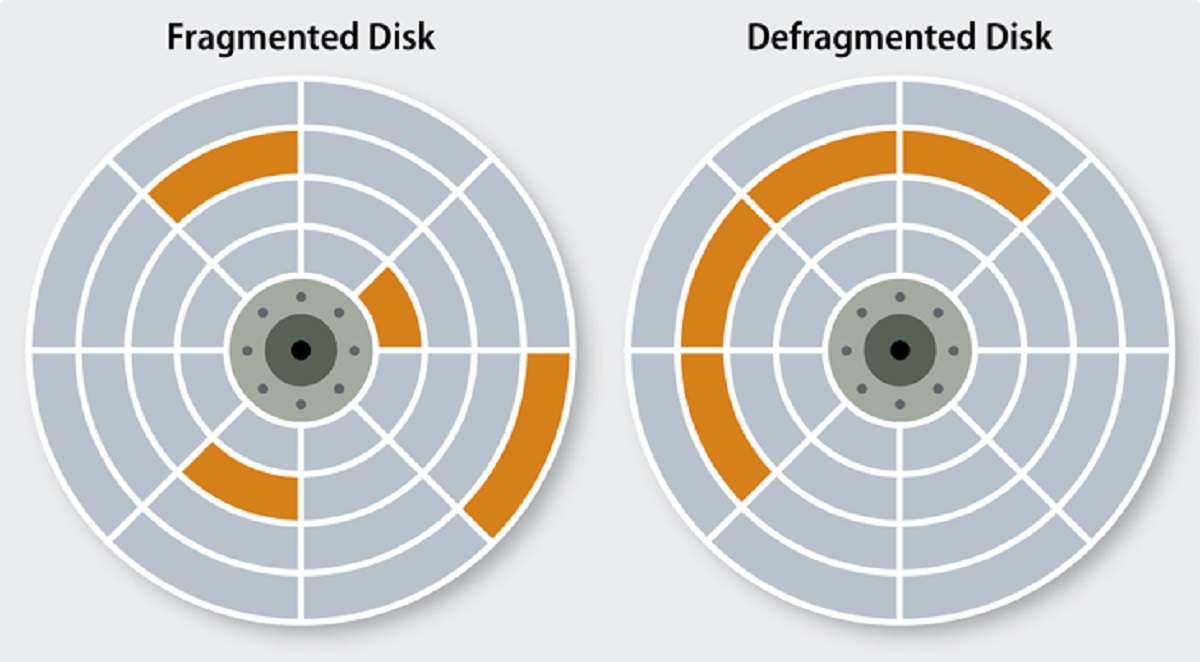
Disk fragmentation is a consequence of how a mechanical hard disk writes and arranges data. Consider an empty hard disk to be a new blank exercise book. When you first copy files to it, they are all arranged to start from the first page towards the last. However, as time moves, you may need to delete a file or move it from one folder to another. Now, if you delete a file that was stored close to page 1 you will have some free empty space in the middle of other existing data. Now imagine repeating those delete operations over and over. You end up with gaps of unwritten spaces scattered all over the drive. Now let’s assume at this point you bring in a relatively huge file to this hard drive. What will happen is that the computer will first place part of the huge file in the free available gaps until they are all filled up. Then whatever remains will be pushed to the back pages where there’s unwritten space. This subdivision of a file within a hard drive is what is referred to as file fragmentation. The main side effect of file fragmentation is a significant slow down of the read times of a mechanical hard drive. This is because the platters have to physically spin faster to access the scattered files. Related Article: 10 easy ways to Speed Up your slow computer
How Defragmentation Works
Disk Defragmentation will undo the effects of a fragmented disk in two ways
During Defragmentation, any files that have been split up and spread all over will be reassembled to one location which will see a performance gain in access times.After running Disk Defragmentation, most of the available free space is arranged in one large continuous piece thus new files written will not be fragmented.
Related Article: Windows User Account Control (UAC) Explained
SSD Optimization
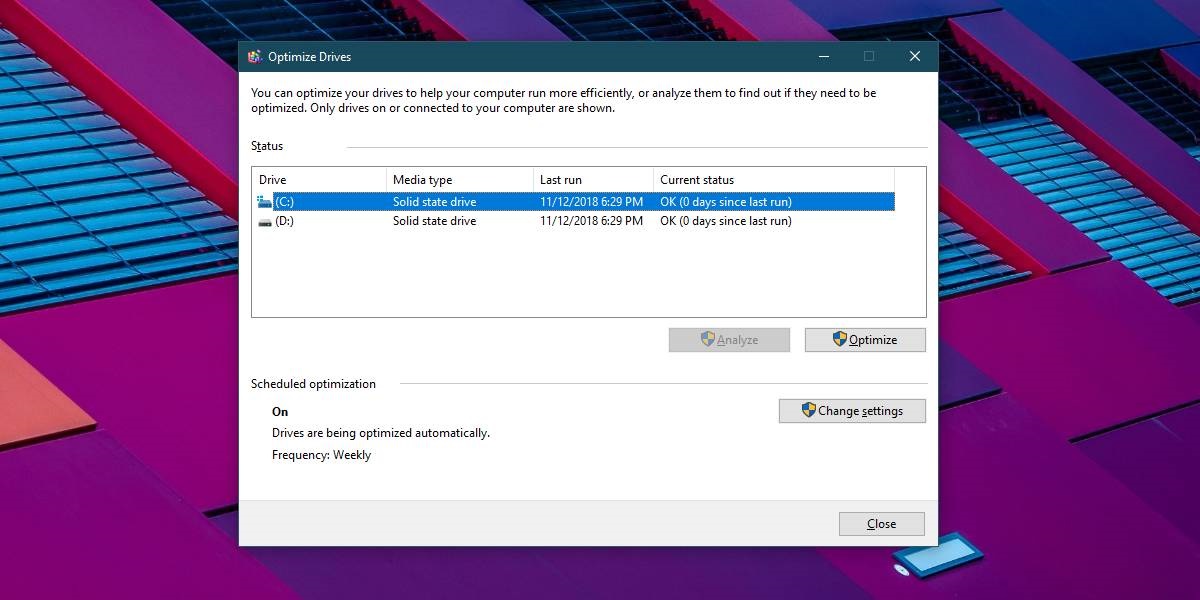
You may wonder if your Solid State Drive (SSD) suffers from similar predicaments. The short answer is, No, SSDs do not lose performance due to file fragmentation. Consequently, this means disk defragmentation will not result in similar performance benefits as with mechanical hard disks. A PC can access all data within an SSD at the same speed. That is regardless of which chip the data is stored at because SSDs do not have any moving parts. Actually, running disk defragmentation on an SSD causes more harm than good. See, SSDs have a finite number of write cycles before it wears out completely. Disk Defragmentation operations will use up a lot of those cycles. This is why all Windows versions after Windows 7 don’t allow you to defragment any SSD. Instead, they only provide the option to optimize the SSD using a command called “Trim Command”. Read More: How to delete Windows 10 inbuilt apps The Trim Command helps the SSD perform write operations much faster in the future. Unlike Disk Defragmentation, Trim is an automated function in windows that runs periodically so you don’t have to keep doing it.